
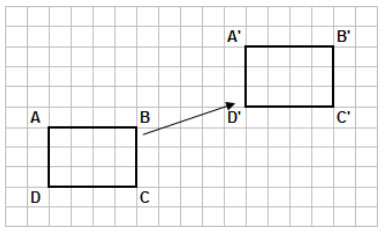
A translation maps points R to R at (-4,8). What translation maps TUVW onto TUVW (x,y) -> (x-3, y+7) Which of the following is true for an isometry The pre-image and the image are congruent RSV has coordinates R (2,1), S (3,2), and V (2,6). When plotting the new graph it works the same, now the new points will have to be a times further from the y-axis. The translation (x,y) -> (x+3, y-7) maps TUVW onto TUVW. When stretching parallel to the x-axis with factor a you substitute every x elke x in the function by ( 1 a x). The graph of function f ( x) = x 2 – 1 is stretched parallel to the y-axis with factor 2.Īll points of the new graph will be twice as far from the x-axis. Mind the brackets around the old formula! The graph will be a times further from the x-axis. When stretching parallel to the y-axis with a factor a all outcomes of a formula are multiplied with a. You can change a graph by multiplying it with a certain number. The new function is g( x) = 2( x + 5) 2 + 3( x + 5).īy removing brackets you will get: g( x) =įor a translation to the right with p and upwards with q, you will get translation ( p, q).įor the standard formula y = ax n then new formula will be: y = a( x – p) n + q. The function f ( x) = 2 x 2 + 3 x is translated 5 units to the left. In that case you will get ( x – (–…)) = ( x + …).įor the graphs it works the same as above, only now you have to read off every point and you will have to plot the new points p to the right. When a transformation is performed, the original shape is called the preimage. When translating a formula or graph horizontally to the right with p, you change every x in the old formula with ( x – p). What are transformations in geometry Transformations in geometry are changes to a geometric figure or shape. The above video is from a third-party source. This is an essential Maths and Geometry skill to help them to understand shape location, translation and transformation.
The function for the new graph is g( x) = x 3 + 4. This worksheet will teach your child to successfully translate shapes on both squared paper and a grid, without altering them in terms of size or rotation.

Translation along the x-axis involves adding or subtracting a constant value to the every x coordinate in the shape be transformed, which effectively moves the shape horizontally. This is essentially moving (or 'sliding') the shape as-is from one position to another. Just read off every value, add q and plot the new graph.īelow you can see how function f ( x) = x 3 is translated upwards by 4. The simplest type of transformation is translation. To plot the new graph from the old graph is easy. A transformation is a way of changing the size or position of a shape. To translate a formula vertically with q, you just add + q behind the formula. Translation is an example of a transformation. Translating positively in the x-axis would shift the image to the right. You can change a graph by moving it vertically or horizontally. Translations: Meaning Types Geometry Formula Algebra Examples. Formulas, graphs & relations » Mutations on formulas and graphs (translating and stretching)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
